

When buying a telescope, a very important thing to consider is the mount. Their advantage is that they are shorter, therefore more portable, but still have a large aperture for gathering more light. The eyepiece is often in the bottom end like a refractor. Catadioptrics or "compound" telescopes tend to be short and fat. Reflecting telescopes are often called Newtonian telescopes.Ī catadioptric telescope uses mirrors and lenses. The eyepiece is usually on the side near the top rather than at the bottom. They tend to be fatter than refractors but just as long. They tend to be long and skinny.Ī reflecting telescope uses mirrors and was invented by Sir Isaac Newton. This was the type Galileo used 400 years ago. The refractor is the stereotypical telescope. Reflecting scopes use mirrors and catadioptric scopes use a combination of lenses and mirrors. But if you could improve their clarity, using diffractive lenses instead of mirrors or refractive lenses would allow a space telescope to be much cheaper, lighter, and larger.First off, there are three basic types of telescopes: refracting, reflecting and catadioptric. Thin, simple diffractive lenses are notorious for their blurry images, so they have never been used in astronomical observatories. Today, similar diffractive lenses can be found in many small-sized consumer optics-from camera lenses to virtual reality headsets.

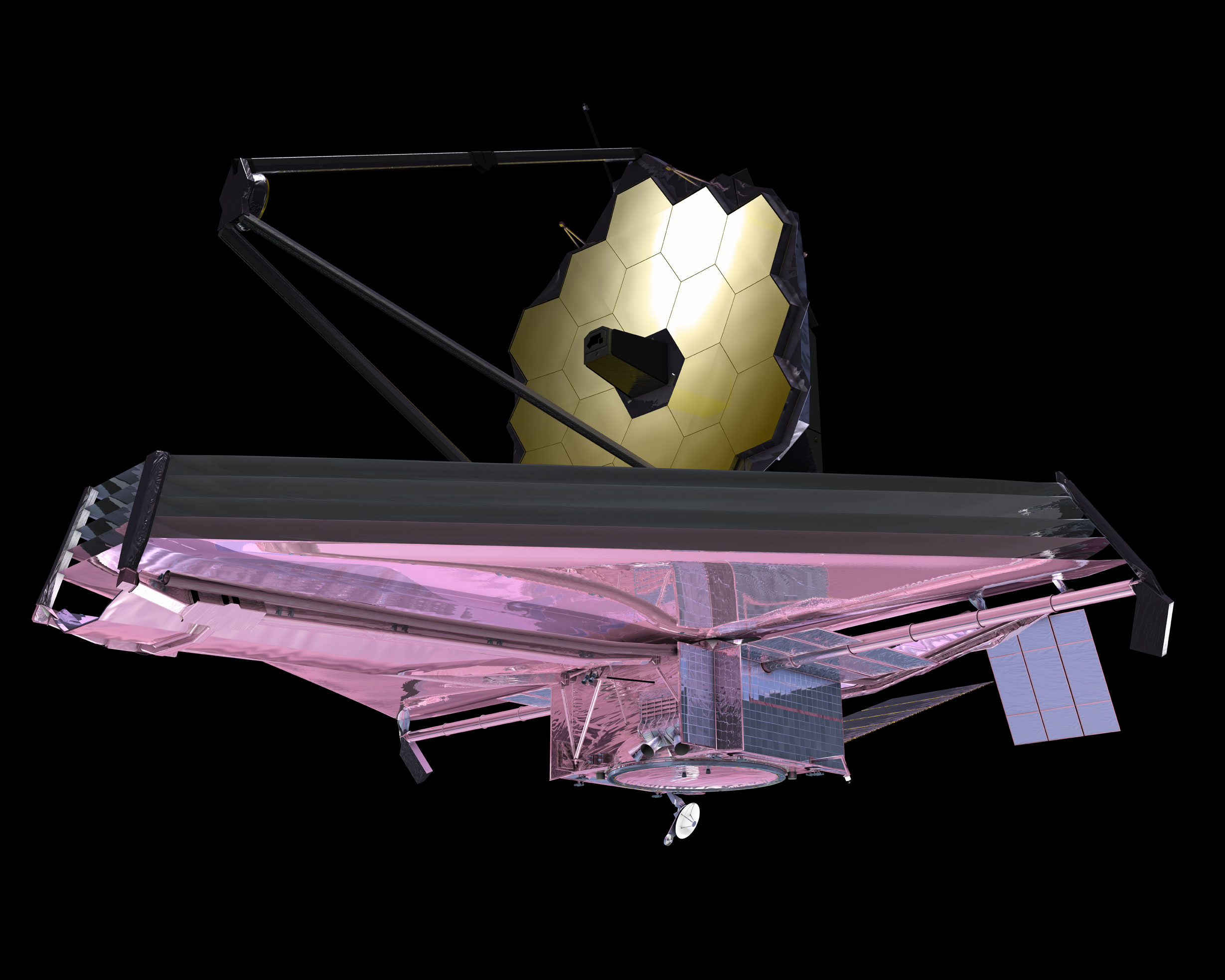
The first such lenses were invented by the French scientist Augustin-Jean Fresnel in 1819 to provide lightweight lenses for lighthouses. A cleverly arranged pattern of steps and angles on a glass surface can form a diffractive lens. In contrast, diffraction is when light bends around corners and obstacles. Refraction is when light changes direction as it passes from one medium to another-it is the reason light bends when it enters water. To bypass this bottleneck, a few of us came up with the idea of revisiting an old technology called diffractive lenses.Ĭonventional lenses use refraction to focus light. In our discussions, we realized that a major bottleneck preventing the construction of more powerful telescopes is the challenge of making larger mirrors and getting them into orbit. In 2016, aerospace giant Northrop Grumman invited me and 14 other professors and NASA scientists-all experts on exoplanets and the search for extraterrestrial life-to Los Angeles to answer one question: What will exoplanet space telescopes look like in 50 years? These ambitious telescope projects are always expensive, laborious, and produce a single powerful-but very specialized-observatory. The next flagship telescope is not expected to fly before 2045 and is estimated to cost $11 billion. The James Webb Space Telescope cost more than $8 billion and took over 20 years to build. Because of these differences, it would be possible to launch many individual units into orbit and create a powerful network of telescopes. Our proposed telescope, the Nautilus Space Observatory, would replace large, heavy mirrors with a novel, thin lens that is much lighter, cheaper, and easier to produce than mirrored telescopes. For the last seven years, I have been co-leading a team that is developing a new kind of space telescope that could collect a hundred times more light than the James Webb Space Telescope, the biggest space telescope ever built.Īlmost all space telescopes, including Hubble and Webb, collect light using mirrors.

I am an astronomer who studies astrobiology and planets around distant stars. To find the answer, astronomers will likely need more powerful telescopes than exist today. The grand question is whether any of these planets are home to life. Katie Yung, Daniel Apai/University of Arizona, AllThingsSpace/SketchFab, CC BY-ND reader comments 162 withĪstronomers have discovered more than 5,000 planets outside of the solar system to date.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
